Last updated on May 17th, 2024
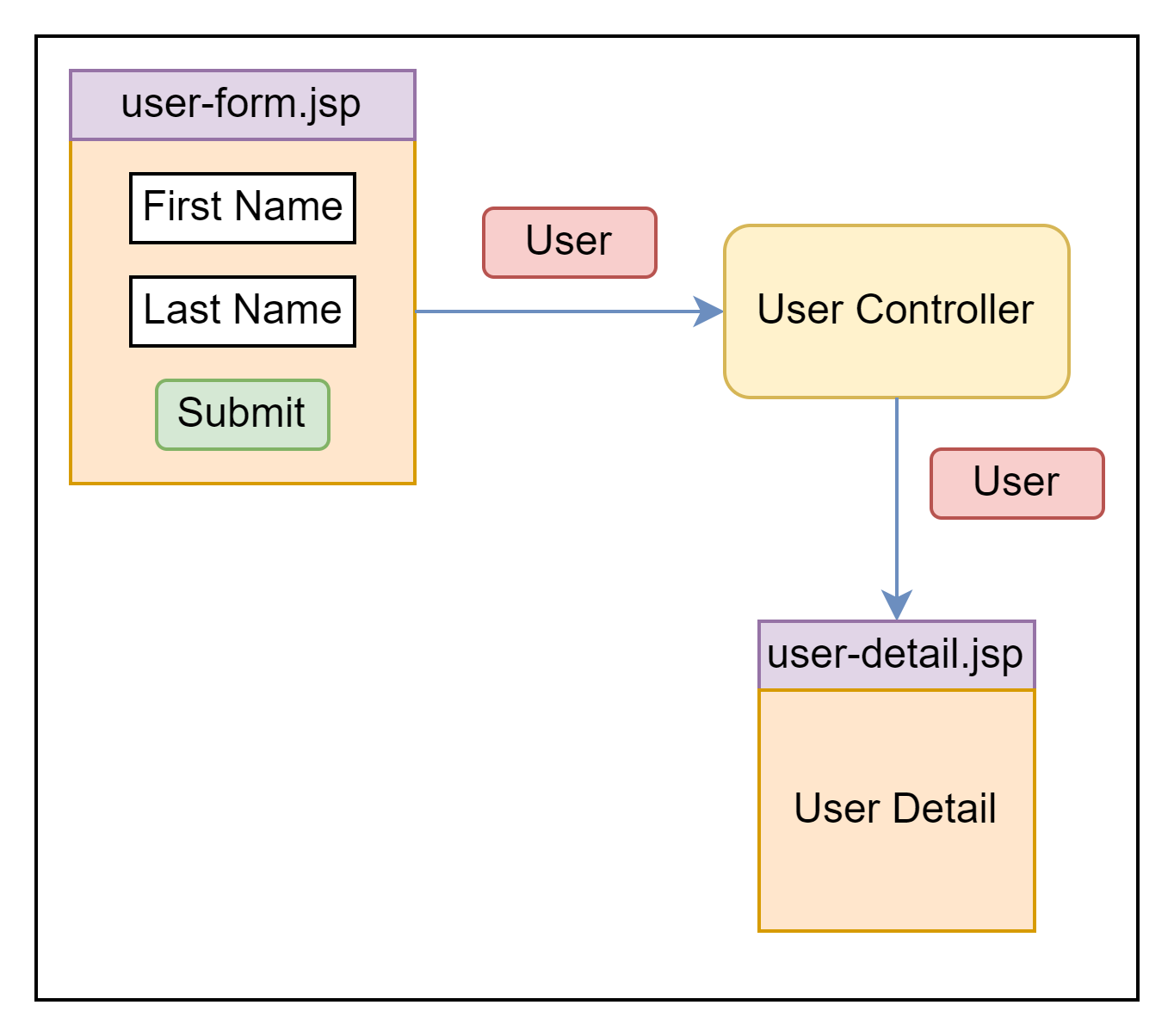
In this example, we create a form for user input and show user detail through the Spring MVC form tag.
<form:input path=""> This is provided by the Spring MVC form tag for the text field.
Development Process:
1. Keep Eclipse IDE ready
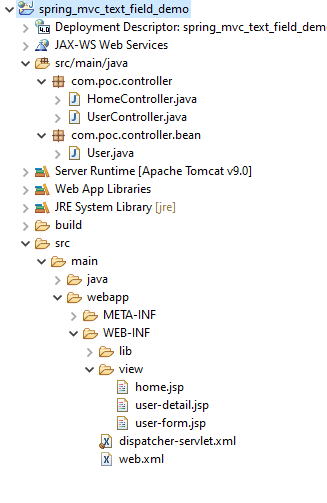
2. Project Structure
3. Add the jar file
4. Configure Spring DispacherServlet
5. Add configuration to a file
6. Create View Page
7. Create Bean Class
8. Create Controller Class
9. Run the App
1. Keep Eclipse IDE ready
2. Project Structure
3. Add the jar file
common-logging-<version>.jar
spring-aop-<version>.jar
spring-context-<version>.jar
spring-core-<version>.jar
spring-expression-<version>.jar
spring-web-<version>.jar
spring-webmvc-<version>.jar4. Create View Page
home.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<body>
<a href="http://localhost:8080/spring_mvc_text_field_demo/user/showForm">Click For User Form</a>
</body>
</html>user-form.jsp:
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>User Registration Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form action="processForm" modelAttribute="user">
First name: <form:input path="firstName" />
<br>
<br>
Last name: <form:input path="lastName" />
<br>
<br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>→ When the form is loaded Spring MVC will call the user.getXXX() method.
→ When clicking the submit button then Spring MVC will call the user.setXXX(-) method
→ <form:input path=”firstName” /> this firstName is a bean class property name.
user-detail.jsp:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>User Detail</title>
</head>
<body>User Detail: ${user.firstName} ${user.lastName}
</body>
</html>5. Configure Spring DispacherServlet
web.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4.xsd"
id="WebApp_ID" version="4.0">
<display-name>spring-mvc-text-field-demo</display-name>
<absolute-ordering />
<!-- Spring MVC Configs -->
<!-- Configure Spring MVC Dispatcher Servlet -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!-- Set up URL mapping for Spring MVC Dispatcher Servlet in this example -->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>→ This file is created in the WEB-INF directory in this application.
6. Add configuration to file
dispatcher-servlet.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- Add support for component scanning -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.poc" />
<!-- Add support for conversion, formatting and validation support -->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!-- Define Spring MVC view resolver -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/view/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
</beans>7. Create Bean Class
User.java:
package com.poc.controller.bean;
public class User {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public User() {
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}8. Create Controller Class
HomeController.java:
package com.poc.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String showPage() {
return "home";
}
}UserController.java:
package com.poc.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.poc.controller.bean.User;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController{
@RequestMapping("/showForm")
public String showForm(Model theModel) {
// create a User object
User user=new User();
// add user object to the model
theModel.addAttribute("user",user);
return "user-form";
}
@RequestMapping("/processForm")
public String processForm(@ModelAttribute("user") User user) {
return "user-detail";
}
}→ Model is used to move data between controllers and views.
→ “theModel.addAttribute(“attribute_name”, “value”)” is used for data wrapping to the view form.
→ <form:form modelAttribute=”attribute_name”> in this we can use attribute name that we added Model attribute name like theModel.addAttribute(“user”,user).
→ @ModelAttribute is wrapping form data to object.
9. Run the App
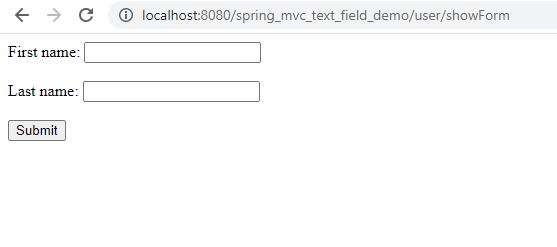
Conclusion:
This example explains How to use the <form:input/> tag. How to bind data in the Spring MVC form tag? What is the use of the Model? What is the use of @ModelAttribute?
