Last updated on April 27th, 2024
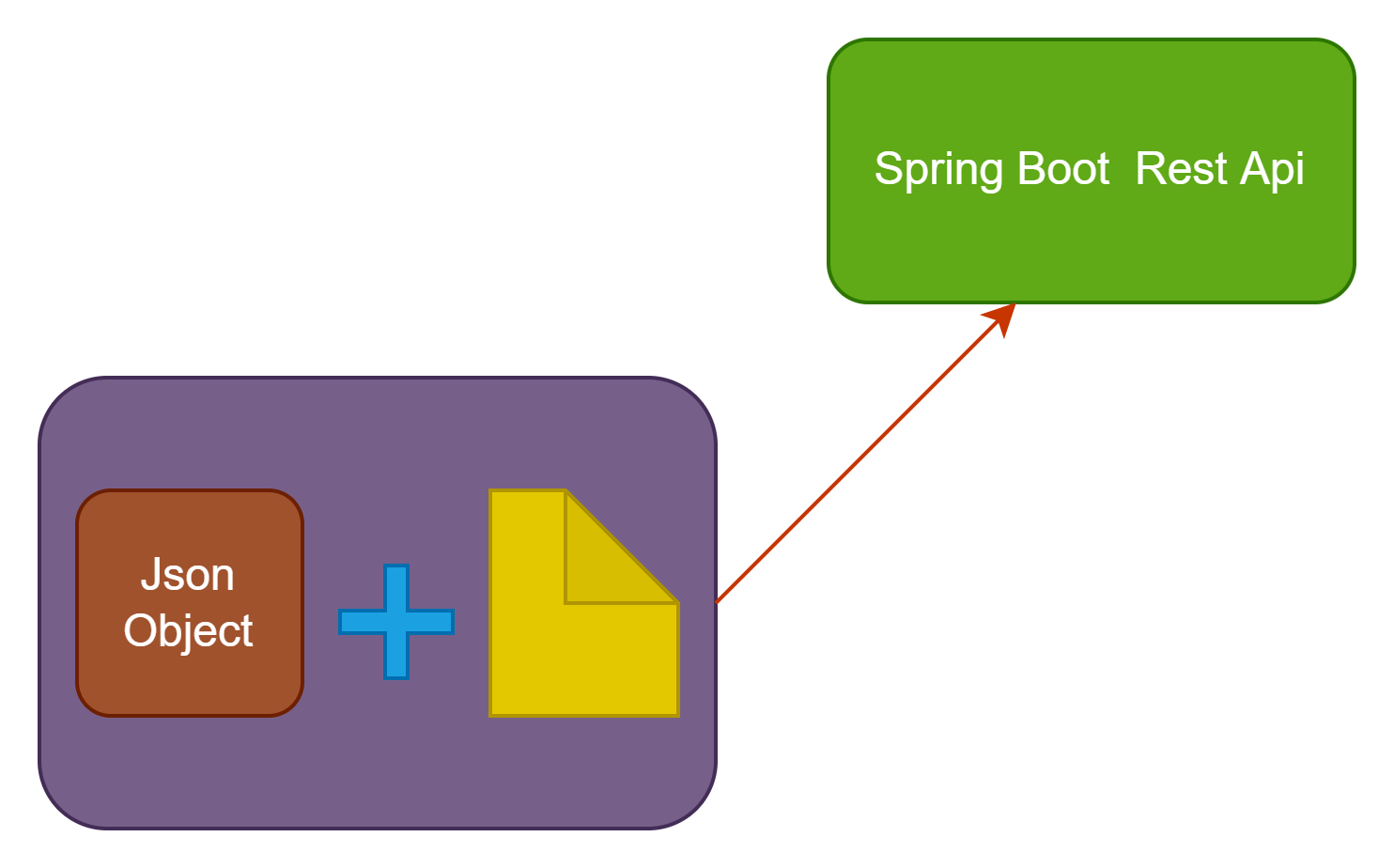
Wn can send a JSON object with file upload in a single API endpoint in the Spring Boot REST by using the ObjectMapper class. When we are working on a real-time project at that time we have scenarios like user registration with an image, adding a product with an image, add some data with the file into the database through rest API—this kind of scenario we achieve with the help of the ObjectMapper class.
In this topic, we will learn how to send a JSON object with file upload with the help of the ObjectMapper to the Spring Boot Rest API endpoint. ObjectMapper class is helping to convert JSON to Java class and vice versa.
Development Process:
1. Keep Eclipse IDE ready(STS Integrated)
2. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
3. Configure Object Mapper
4. Enable Multipart File configuration in the application.properties file
5. Create a FileStorage class
6. Create a Service
7. Create a Rest Controller class
8. Run the Project
1. Keep Eclipse IDE ready(STS Integrated)
Refer to this article How to Create Spring Project in IDE to create Spring Boot Project in Eclipse IDE.
2. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
Add the following dependencies:
• Spring Web
• Spring Configuration Processor
Maven Dependency
pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
<relativePath/>
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>Json_Object_With_File_Spring_Boot_Rest_Api</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>Json_Object_With_File_Spring_Boot_Rest_Api</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3. Configure Object Mapper
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
@SpringBootApplication
public class JsonObjectWithFileSpringBootRestApiApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(JsonObjectWithFileSpringBootRestApiApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ObjectMapper getObjectMapper() {
return new ObjectMapper();
}
}4. Enable Multipart File configuration in the application.properties file
## MULTIPART (MultipartProperties)
# Enable multipart uploads
spring.servlet.multipart.enabled=true
# Threshold after which files are written to the disk.
spring.servlet.multipart.file-size-threshold=2KB
# Max file size.
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=500KB
# Max Request Size
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=500KB
## File Storage Properties
file.upload-dir=./uploads
server.port=80825. Create a FileStorage class
FileStorageProperties.java:
package com.example.property;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "file")
public class FileStorageProperties {
private String uploadDir;
public String getUploadDir() {
return uploadDir;
}
public void setUploadDir(String uploadDir) {
this.uploadDir = uploadDir;
}
}→ @ConfigurationProperties allows mapping the entire Properties and Yaml files into an object. By default, this annotation reads values from the application.properties file.
6. Create a Service
FileStorageService.java:
package com.example.service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardCopyOption;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import com.example.property.FileStorageProperties;
@Service
public class FileStorageService {
private final Path fileStorageLocation;
@Autowired
public FileStorageService(FileStorageProperties fileStorageProperties) {
this.fileStorageLocation = Paths.get(fileStorageProperties.getUploadDir()).toAbsolutePath().normalize();
try {
Files.createDirectories(this.fileStorageLocation);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Couldn't create the directory where the upload files will be saved.", ex);
}
}
public String storeFile(MultipartFile file) {
// Normalize file name
String fileName = StringUtils.cleanPath(file.getOriginalFilename());
try {
// Check if the file's name contains valid characters or not
if (fileName.contains("..")) {
throw new RuntimeException("Sorry! File name which contains invalid path sequence " + fileName);
}
// Copy file to the target place (Replacing existing file with the same name)
Path targetLocation = this.fileStorageLocation.resolve(fileName);
Files.copy(file.getInputStream(), targetLocation, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
return fileName;
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}7. Create a Rest Controller class
UserController.java:
package com.example.api;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.ServletUriComponentsBuilder;
import com.example.response.User;
import com.example.service.FileStorageService;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private FileStorageService fileStorageService;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@PostMapping("/json-object-file-upload")
public User uploadFile(@RequestParam("model") String jsonObject, @RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
User response = null;
try {
String fileName = fileStorageService.storeFile(file);
ServletUriComponentsBuilder.fromCurrentContextPath().path(fileName).toUriString();
response = objectMapper.readValue(jsonObject, User.class);
response.setImage(file.getOriginalFilename());
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return response;
}
}8. Run the Project
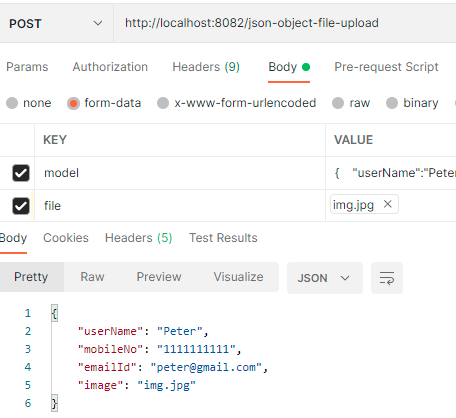
JSON:
{
"userName":"Peter",
"mobileNo":"1111111111",
"emailId":"peter@gmail.com"
}→ JSON is a simple string format. It can be understood by us and technologies.
→ “{ }” represents a JSON object.
→ “[ ]” represents a JSON array.
We can test API via postman.
POST type: http://localhost:8082/json-object-file-upload
Conclusion:
This example explains How to send the JSON object with a file in the Spring Boot Rest API? What is an Object Mapper? How to configure an Object Mapper? How to convert JSON to Java class through Object Mapper?
