Last updated on March 14th, 2024
This topic teaches us how to implement the many-to-one bidirectional mapping between two JPA entities using Spring Boot, Spring Data JPA, H2 database and Lombok. This kind of mapping provides navigation in both directions(one entity to another and vice-versa). We can achieve this mapping by combining two(one-to-many and many-to-one) mappings. We will also achieve one-to-many bidirectional mapping with the same combination of these two mappings. The diagram representation of this kind of bidirectional mapping is shown below.
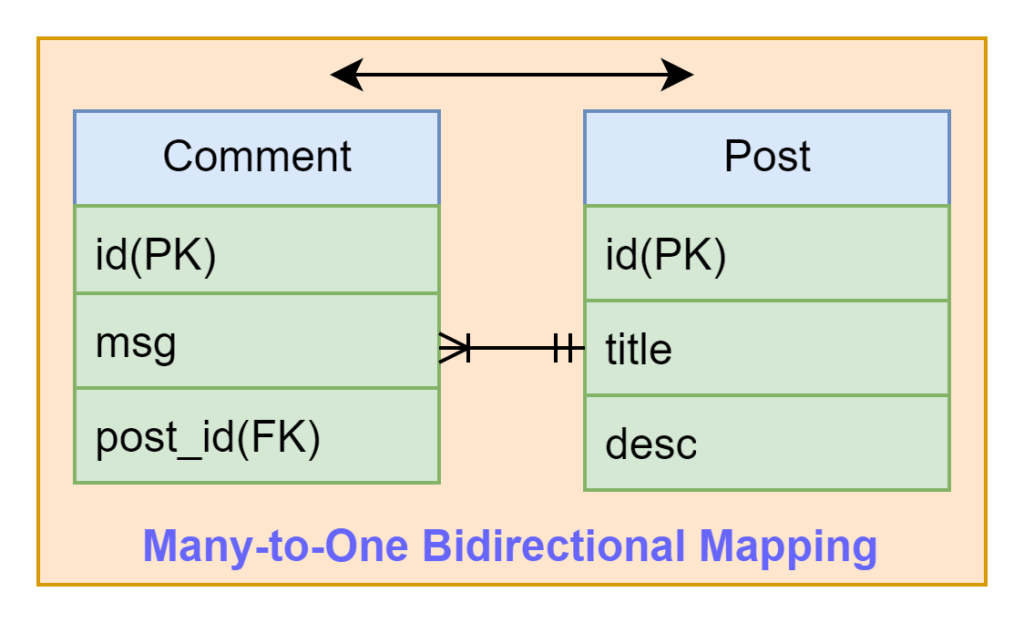
We will create a restful web service example to implement this mapping using the Spring Boot application step-by-step. Let’s begin to implement
Table of Contents
1. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
2. Maven Dependency
3. Define the H2 database configuration
4. Create Entity
5. Create Repository
6. Create Service
7. Create Controller
8. Run the Spring Boot application
9. Conclusion
1. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
Add the following dependencies:
• Spring Web
• Lombok
• H2 Database
• Spring Data JPA
Project Structure of Many-To-One Bidirectional Mapping
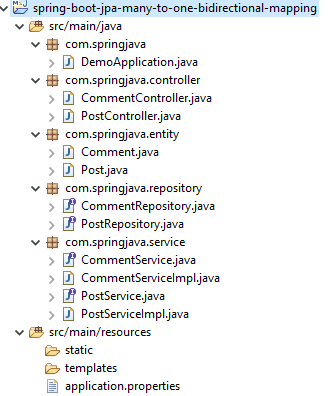
2. Maven Dependency
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.springjava</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3. Define the H2 database configuration
We are configuring the H2 database configuration in the application.properties file.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:test
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.h2.console.enabled=true4. Create Entity
Post.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@Entity
public class Post {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String desc;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "post")
@JsonIgnoreProperties("post")
private List < Comment > commentList;
}→ We used @OneToMany annotation in this class to make the one-to-many relationship with the Comment JPA entity class. We used the mappedBy attribute to specify the referencing side for the mapping.
→ This @JsonIgnoreProperties annotation is used to mark the property that Jackson ignored.
Comment.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@Entity
public class Comment {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String msg;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "post_id", referencedColumnName = "id")
@JsonIgnoreProperties("commentList")
private Post post;
}→ This @ManyToOne annotation is used to make the relationship with the Post JPA entity class.
→ This @JoinColumn annotation defines a foreign key column(post_id) with the mentioned name in this entity.
→ This @Data annotation is used to generate a constructor, setter method, getter method, etc. for the Java Bean class.
5. Create Repository
PostRepository.java
package com.springjava.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springjava.entity.Post;
public interface PostRepository extends JpaRepository<Post, Integer> {
}CommentRepository.java
package com.springjava.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springjava.entity.Comment;
public interface CommentRepository extends JpaRepository<Comment, Integer> {
}6. Create Service
PostService.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.springjava.entity.Post;
public interface PostService {
void save(Post post);
List<Post> getPostList();
Post findById(Integer id);
}PostServiceImpl.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springjava.entity.Post;
import com.springjava.repository.PostRepository;
@Service
public class PostServiceImpl implements PostService {
@Autowired
PostRepository postRepo;
@Override
public void save(Post post) {
postRepo.save(post);
}
@Override
public List < Post > getPostList() {
return postRepo.findAll();
}
@Override
public Post findById(Integer id) {
return postRepo.findById(id).get();
}
}CommentService.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.springjava.entity.Comment;
public interface CommentService {
void save(Comment comment);
List<Comment> findAll();
}CommentServiceImpl.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springjava.entity.Comment;
import com.springjava.repository.CommentRepository;
@Service
public class CommentServiceImpl implements CommentService {
@Autowired
CommentRepository commentRepo;
@Override
public void save(Comment comment) {
commentRepo.save(comment);
}
@Override
public List < Comment > findAll() {
return commentRepo.findAll();
}
}7. Create Controller
PostController.java
package com.springjava.controller;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.springjava.entity.Post;
import com.springjava.service.PostService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PostController {
@Autowired
PostService postService;
@PostMapping("/post/save")
public ResponseEntity < ? > save(@RequestBody Post post) {
Map < String, Object > respPost = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
// saving Post into db
postService.save(post);
respPost.put("status", 1);
respPost.put("message", "Record is Saved Successfully!");
return new ResponseEntity < > (respPost, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@GetMapping("/post/list")
public ResponseEntity < ? > getPosts() {
Map < String, Object > respPost = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
List < Post > postList = postService.getPostList();
if (!postList.isEmpty()) {
respPost.put("status", 1);
respPost.put("data", postList);
return new ResponseEntity < > (respPost, HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
respPost.clear();
respPost.put("status", 0);
respPost.put("message", "Data is not found");
return new ResponseEntity < > (respPost, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
}CommentController.java
package com.springjava.controller;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.springjava.entity.Comment;
import com.springjava.entity.Post;
import com.springjava.service.CommentService;
import com.springjava.service.PostService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class CommentController {
@Autowired
PostService postService;
@Autowired
CommentService commentService;
@PostMapping("/comment/{postId}/save")
public ResponseEntity<?> saveComment(@PathVariable("postId") Integer id, @RequestBody Comment comment) {
Map<String, Object> respComment = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
Post post= postService.findById(id);
comment.setPost(post);
commentService.save(comment);
respComment.put("status", 1);
respComment.put("message", "Record is Saved Successfully!");
return new ResponseEntity<>(respComment, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@GetMapping("/comment/list")
public ResponseEntity<?> getComments() {
Map<String, Object> respComment = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
List<Comment> commentList=commentService.findAll();
if (!commentList.isEmpty()) {
respComment.put("status", 1);
respComment.put("data", commentList);
return new ResponseEntity<>(respComment, HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
respComment.clear();
respComment.put("status", 0);
respComment.put("message", "Data is not found");
return new ResponseEntity<>( respComment, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
}8. Run the Spring Boot application
To run this Spring Boot application of this bidirectional mapping we will Right-click on the DemoApplication.java and then click on Run As after that select Java Application.
To test the API on the Postman
Url: http://localhost:8080/api/post/save
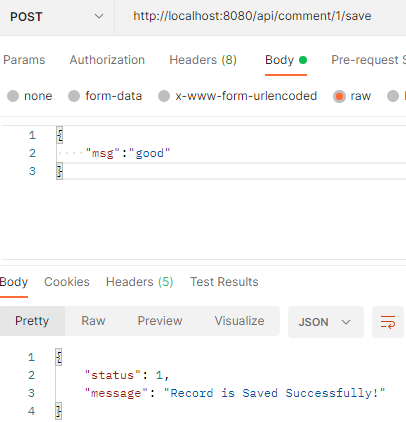
Url: http://localhost:8080/api/comment/1/save
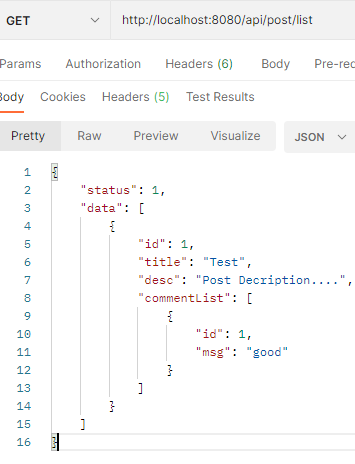
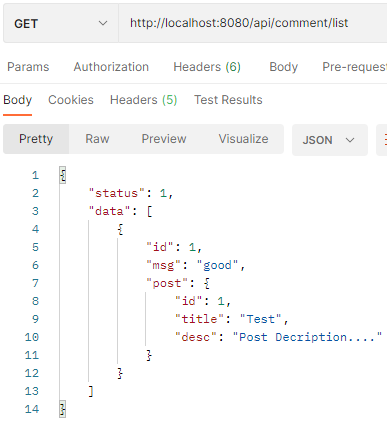
Url: http://localhost:8080/api/post/list
Url: http://localhost:8080/api/comment/list
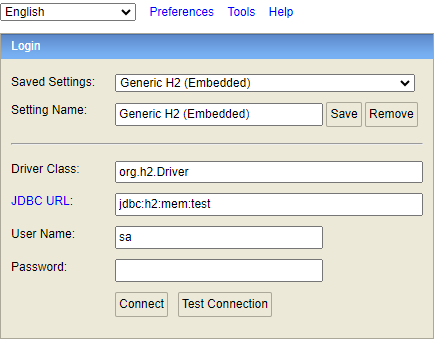
To check the H2 database we can browse this URL “http://localhost:8080/h2-console” on the browser to view the tables in the database which are created by this spring boot application.
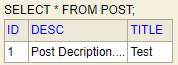
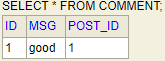
See both tables below here:
9. Conclusion
In this topic, we learnt about how to implement many-to-one bidirectional mapping in spring boot, spring data JPA, Lombok and H2 database with rest API example.
