Last updated on October 4th, 2024
In the Spring Boot Application, if we need to handle exceptions globally, we can define a class that is annotated with @ControllerAdvice annotation and define methods in that class which is annotated with @ExceptionHandler annotation. In this topic, how to use @ControllerAdvice and @ExceptionHandler annotation to use global exception handling in Spring Boot Rest API.
We will create a CRUD restful web service example to implement Global Exception handling in Spring Boot Application using Spring Web, Maven, Spring Data JPA and MySql.
These are the following steps:
1. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
2. Keep Eclipse IDE ready
3. Defining Configuration
4. Creating a JPA Entity class
5. Creating a JPA Repository
6. Creating an Error Model class
7. Creating a Custom Exception class
8. Creating a Global Exception Handler class
9. Creating a Service
10. Creating a Rest Controller class
11. Run the Project
1. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
We are creating a Spring Boot Application from the web tool Spring Initializr or you can create it from the IDE(STS, VS Code etc.) you are using.
Add the following dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Data JPA
- Mysql Driver
2. Keep the IDE ready
We are importing this created application into our Eclipse IDE or you can import it into another IDE you are using. You can refer to this article to create and set up the Spring Boot Project in Eclipse IDE.
Project Structure of Global Exception Handling in Spring Boot Rest API
Maven Dependency
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.poc</groupId>
<artifactId>Global_Exception_Handle_Spring_Boot_Rest_Api</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Global_Exception_Handle_Spring_Boot_Rest_Api</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3. Defining Configuration
We are configuring the MySql database configuration in the application.properties file.
application.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user_db?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=true
spring.jpa.show-sql=true4. Creating a JPA Entity class
We are creating a JPA entity class User with properties(id, userName, mobileNo, emailId, city, password).
User.java
package com.poc.rest.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String mobileNo;
private String emailId;
private String city;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getMobileNo() {
return mobileNo;
}
public void setMobileNo(String mobileNo) {
this.mobileNo = mobileNo;
}
public String getEmailId() {
return emailId;
}
public void setEmailId(String emailId) {
this.emailId = emailId;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}5. Creating a JPA Repository
We are a JPA Repository to communicates with a database table and performs persistence operations with query methods(save(), findById(), findAll(), and delete()).
UserRespository.java
package com.poc.rest.repo;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.poc.rest.entity.User;
public interface UserRepstry extends JpaRepository < User, Integer > {
}6. Creating an Error Model class
We are creating an error model class ErrorDetail.
ErrorDetails.java
package com.poc.rest.exception;
public class ErrorDetails {
private Integer status;
private String message;
public ErrorDetails(Integer status, String message) {
super();
this.status = status;
this.message = message;
}
public Integer getStatus() {
return status;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}7. Creating a Custom Exception class
We are creating a custom exception class UserNotFoundException and this class is annotated with @ResponseStatus annotation.
UserNotFoundException.java
package com.poc.rest.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(value = HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class UserNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public UserNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}→ @ResponseStatus: Marks a method or exception class with the status code() and reason() that should be returned. A status code is applied to the HTTP response when the handler method is invoked and overrides status information detail set by the other means, like ResponseEntity or “redirect:”.
8. Creating a Global Exception Handler class
We are creating a global exception handler class GlobalExceptionHandler and this class is annotated with @ControllerAdvice and extends the ResponseEntityExceptionHandler class.
package com.poc.rest.exception;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ResponseEntityExceptionHandler;
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity < ErrorDetails > userNotFoundException(UserNotFoundException ex) {
ErrorDetails errorModel = new ErrorDetails(0, ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity < ErrorDetails > (errorModel, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity < ? > globleExcpetionHandler(Exception ex) {
ErrorDetails errorModel = new ErrorDetails(0, ex.getMessage());
return new ResponseEntity < > (errorModel, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}→ @ControllerAdvice is a specialization of the @Component annotation which authorizes to handling of exceptions across the whole application in one global exception-handling component. It can act as an interceptor of exceptions that are thrown by methods.
→ ResponseEntityExceptionHandler is a convenient base class for @ControllerAdvice classes that wish to provide centralized exception handling across all @RequestMapping methods through the @ExceptionHandler methods of our application. This base class provides an @ExceptionHandler method for handling internal Spring MVC exceptions that are raised on the application. This method returns a ResponseEntity for writing to the response with a message converter, in contrast to DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver which returns the output as the ModelAndView.
→ @ExceptionHandler is an annotation that is used for handling exceptions in the specific handler classes or the handler methods.
9. Creating a Service
We are creating a service interface UserService with some method declaration.
UserService.java
package com.poc.rest.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.poc.rest.entity.User;
public interface UserService {
public List < User > getTheUsersList();
public void save(User user);
public User findById(Integer id);
public void delete(User user);
}UserServiceImpl.java
package com.poc.rest.service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.poc.rest.entity.User;
import com.poc.rest.exception.UserNotFoundException;
import com.poc.rest.repo.UserRepstry ;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepstry userRepo;
@Override
public List < User > getTheUsersList() {
return userRepo.findAll();
}
@Override
public void save(User user) {
userRepo.save(user);
}
@Override
public User findById(Integer id) {
Optional < User > userInfo = userRepo.findById(id);
User user = null;
if (userInfo.isPresent()) {
user = userInfo.get();
} else {
throw new UserNotFoundException("The user info is not available:" + id);
}
return user;
}
@Override
public void delete(User user) {
userRepo.delete(user);
}
}10. Creating a Rest Controller class
We are creating a Rest Controller class UserController to handler requests from clients and give the response in JSON form.
UserController.java
package com.poc.rest.controller;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.poc.rest.entity.User;
import com.poc.rest.service.UserService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/users")
public ResponseEntity < ? > getUser() {
Map < String, Object > respJsonOutput = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
List < User > userList = userService.getTheUsersList();
if (!userList.isEmpty()) {
respJsonOutput.put("status", 1);
respJsonOutput.put("data", userList);
return new ResponseEntity < > (respJsonOutput, HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
respJsonOutput.clear();
respJsonOutput.put("status", 0);
respJsonOutput.put("message", "Data is not found");
return new ResponseEntity < > (respJsonOutput, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public ResponseEntity < ? > saveUser(@RequestBody User user) {
Map < String, Object > respJsonOutput = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
userService.save(user);
respJsonOutput.put("status", 1);
respJsonOutput.put("message", "Record is Saved Successfully!");
return new ResponseEntity < > (respJsonOutput, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public ResponseEntity < ? > getUserById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
Map < String, Object > respJsonOutput = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
User user = userService.findById(id);
respJsonOutput.put("status", 1);
respJsonOutput.put("data", user);
return new ResponseEntity < > (respJsonOutput, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{id}")
public ResponseEntity < ? > deleteUser(@PathVariable Integer id) {
Map < String, Object > respJsonOutput = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
User user = userService.findById(id);
userService.delete(user);
respJsonOutput.put("status", 1);
respJsonOutput.put("message", "Record is deleted successfully!");
return new ResponseEntity < > (respJsonOutput, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@PutMapping("/update/{id}")
public ResponseEntity < ? > updateTheUser(@PathVariable Integer id, @RequestBody User userDetail) {
Map < String, Object > respJsonOutput = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
User user = userService.findById(id);
user.setUserName(userDetail.getUserName());
user.setMobileNo(userDetail.getMobileNo());
user.setEmailId(userDetail.getEmailId());
user.setCity(userDetail.getCity());
user.setPassword(userDetail.getPassword());
userService.save(user);
respJsonOutput.put("status", 1);
respJsonOutput.put("data", userService.findById(id));
return new ResponseEntity < > (respJsonOutput, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}11. Run the Project
Right-click on the project’s SpringBootApplication class then click on Run as Java Application.
Test API in the Postman tool
POST: http://localhost:8080/api/save
GET: http://localhost:8080/api/users
GET: http://localhost:8080/api/user/4
PUT: http://localhost:8080/api/update/4
DELETE: http://localhost:8080/api/delete/4
There is no user with id 9.
GET Type: http://localhost:8080/api/user/9
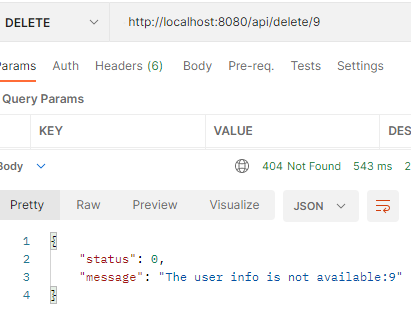
Global exception handles the exception where id is not available.
Conclusion
This example explains How to customize the exception and return a JSON response. How to create a Global Exception Handler class? What is a @ControllerAdvice annotation? What is a @ExceptionHandler annotation? What is a @ResponseStatus?

Good