This topic will teach us to implement one-to-one(@OneToOne annotation) bidirectional mapping using Spring Boot, Hibernate, and Spring Data JPA.
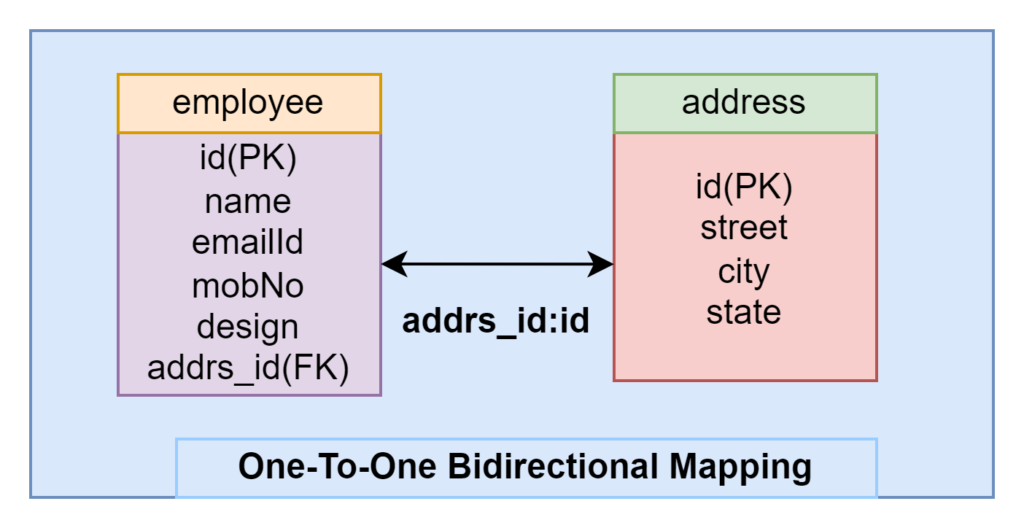
In this example, an employee table is associated with the address table with the help of a foreign key addrs_id which references the address.id using @JoinColumn annotation and also the making relationship between the address table and the employee table using the mappedBy attribute. Then we will get the employees with address details and address with employee details with the help of one-to-one bidirectional mapping.
We will create a restful web service to implement one-to-one bidirectional mapping using Spring Boot.
Table of contents
1. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project for one-to-one Bidirectional Mapping
2. Maven Dependency
3. Define configuration in the application.properties file
4. Create Entity
5. Create Repository
6. Create Service
7. Create Model
8. Create Controller
9. Run the app
10. Conclusion
1. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project for one-to-one Bidirectional Mapping
Add the following dependencies:
• Spring Web
• Lombok
• H2 Database
• Spring Data JPA
2. Maven Dependency
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.springjava</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3. Define configuration in the application.properties file
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:test
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.h2.console.enabled=true4. Create Entity
Address.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import lombok.Data;
@Entity
@Data
public class Address {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String street;
private String city;
private String state;
@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL,mappedBy = "address")
private Employee employee;
}→ The mappedBy attribute is used to specify the referencing side (non-owning side) of the relationship.
Employee.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import lombok.Data;
@Entity
@Data
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String emailId;
private String mobNo;
private String design;
@OneToOne(cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name = "addrs_id")
private Address address;
}→ This @JoinColumn annotation is used on the owning side of the table association to define the foreign key column name and other attributes which are related to the join column.
5. Create Repository
AddressRepository.java
package com.springjava.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springjava.entity.Address;
public interface AddressRepository extends JpaRepository<Address, Integer> { }EmployeeRepository.java
package com.springjava.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springjava.entity.Employee;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> { }6. Create Service
AddressService.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.springjava.entity.Address;
public interface AddressService {
List<Address> findAll();
}AddressServiceImpl.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springjava.entity.Address;
import com.springjava.repository.AddressRepository;
@Service
public class AddressServiceImpl implements AddressService {
@Autowired
AddressRepository addressRepository;
@Override
public List<Address> findAll() {
return addressRepository.findAll();
}
}EmployeeService.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.springjava.entity.Employee;
public interface EmployeeService {
void save(Employee emp);
List<Employee> findAll();
}EmployeeServiceImpl.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springjava.entity.Employee;
import com.springjava.repository.EmployeeRepository;
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@Override
public void save(Employee emp) {
employeeRepository.save(emp);
}
@Override
public List<Employee> findAll() {
return employeeRepository.findAll()
}
}7. Create Model
EmployeeModel.java
package com.springjava.model;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class EmployeeModel {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String emailId;
private String mobNo;
private String design;
private String street;
private String city;
private String state;
}EmployeeController.java
package com.springjava.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.springjava.entity.Address;
import com.springjava.entity.Employee;
import com.springjava.model.EmployeeModel;
import com.springjava.service.AddressService;
import com.springjava.service.EmployeeService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
AddressService addressService;
@Autowired
EmployeeService employeeService;
@PostMapping("/save")
public ResponseEntity < ? > saveEmp(@RequestBody EmployeeModel empModel) {
Map < String, Object > model = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
//creating address object and setting properties
Address address = new Address();
address.setStreet(empModel.getStreet());
address.setCity(empModel.getCity());
address.setState(empModel.getState());
//creating employee object and setting properties
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.setName(empModel.getName());
emp.setEmailId(empModel.getEmailId());
emp.setMobNo(empModel.getMobNo());
emp.setDesign(empModel.getDesign());
emp.setAddress(address);
//saving employee into db
employeeService.save(emp);
model.put("status", 1);
model.put("message", "Record is Saved Successfully!");
return new ResponseEntity < > (model, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@GetMapping("/employees")
public ResponseEntity < ? > getEmployees() {
Map < String, Object > model = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
List < Employee > empList = employeeService.findAll();
List < EmployeeModel > empMList = new ArrayList < > ();
if (!empList.isEmpty()) {
for (Employee emp: empList) {
EmployeeModel empModel = new EmployeeModel();
empModel.setId(emp.getId());
empModel.setName(emp.getName());
empModel.setEmailId(emp.getEmailId());
empModel.setMobNo(emp.getMobNo());
empModel.setDesign(emp.getDesign());
empModel.setStreet(emp.getAddress().getStreet());
empModel.setCity(emp.getAddress().getCity());
empModel.setState(emp.getAddress().getState());
empMList.add(empModel);
}
model.put("status", 1);
model.put("data", empMList);
return new ResponseEntity < > (model, HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
model.clear();
model.put("status", 0);
model.put("message", "Data is not found");
return new ResponseEntity < > (model, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
@GetMapping("/address-list")
public ResponseEntity < ? > getAddressList() {
Map < String, Object > model = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
List < Address > addList = addressService.findAll();
List < EmployeeModel > empMList = new ArrayList < > ();
if (!addList.isEmpty()) {
for (Address address: addList) {
EmployeeModel empModel = new EmployeeModel();
empModel.setId(address.getEmployee().getId());
empModel.setName(address.getEmployee().getName());
empModel.setEmailId(address.getEmployee().getEmailId());
empModel.setMobNo(address.getEmployee().getMobNo());
empModel.setDesign(address.getEmployee().getDesign());
empModel.setStreet(address.getStreet());
empModel.setCity(address.getCity());
empModel.setState(address.getState());
empMList.add(empModel);
}
model.put("status", 1);
model.put("data", empMList);
return new ResponseEntity < > (model, HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
model.clear();
model.put("status", 0);
model.put("message", "Data is not found");
return new ResponseEntity < > (model, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
}9. Run the app
To run this application Right-click on the DemoApplication.java then click on Run As after that select Java Application.
To test the API on the Postman
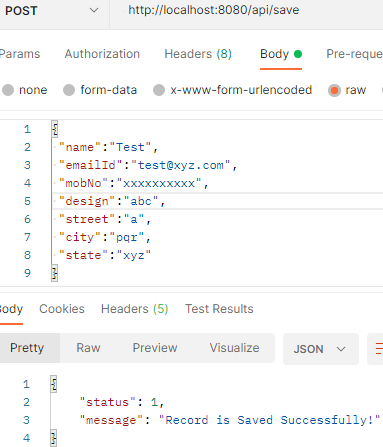
Url: http://localhost:8080/api/save
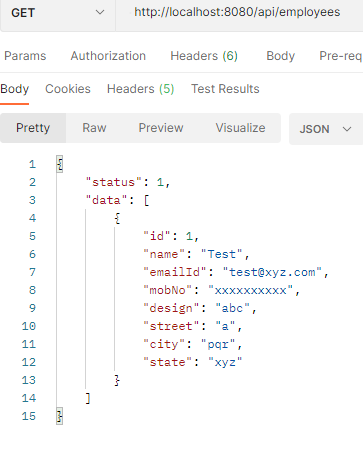
Url: http://localhost:8080/api/employees
Url: http://localhost:8080/api/address-list
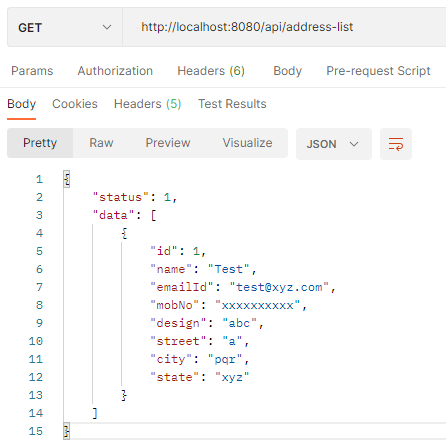
To check the H2 database we can browse this URL “http://localhost:8080/h2-console” on the browser to view the tables in the database which are created by this application.
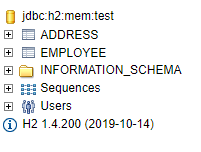
10. Conclusion
In this topic, we learnt how to implement one-to-one bidirectional mapping using the mappedBy attribute in spring boot, spring data JPA, Lombok and H2 database with rest API example.
If you learn about one-to-one unidirectional mapping in the Spring Boot Rest API example click here.
