Last updated on January 16th, 2025
In this example, we will learn how to implement login and registration REST API using spring boot, spring security, hibernate and the H2 database.
We will create an example of Spring Boot REST application where we will build two web services. One web service of user registration and the other is for user login.
Table of Content
1. Keep Eclipse IDE ready(STS integrated)
2. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
3. Maven Dependency
4. Define Database configuration in the application.properties file
5. Create entity class
6. Create a repository
7. Create a service
8. Create a DTO class
9. Create a Controller class
10. Create a Spring Security Config class
11. Insert data in the database using SpringBootApplication class
12. Run the Application
13. Conclusion
1. Keep Eclipse IDE ready(STS integrated)
Refer to this article How to Create Spring Project in IDE to create Spring Boot Project in Eclipse IDE.
2. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
Add the following dependencies:
• Spring Web
• Spring Security
• H2 Database
• Spring Data JPA

3. Maven Dependency
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.11</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.springjava</groupId>
<artifactId>Login_Registration_Rest_Api_Spring_Security</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Login_Registration_Rest_Api_Spring_Security</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>16</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4. Define Database configuration in the application.properties file
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:test
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
server.port=88885. Create entity class
Role.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="roles")
public class Role {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Role() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}User.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import org.hibernate.annotations.LazyCollection;
import org.hibernate.annotations.LazyCollectionOption;
@Entity
@Table(name="users")
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String userName;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String password;
@ManyToMany
@LazyCollection(LazyCollectionOption.FALSE)
private Set<Role> roles;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String username) {
this.userName = username;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Set<Role> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(Set<Role> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
}6. Create a repository
RoleRepository.java
package com.springjava.repository;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springjava.entity.Role;
public interface RoleRepository extends JpaRepository<Role, Integer> {
Optional<Role> findByName(String name);
}UserRepository.java
package com.springjava.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springjava.entity.User;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {
User findByUsernameOrEmail(String username, String email);
}7. Create a service
UserDetail.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springjava.entity.User;
import com.springjava.repository.UserRepository;
@Service
public class UserDetail implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepo;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username)throws UsernameNotFoundException {
User user = userRepo.findByUserNameOrEmail(username, username);
if(user==null){
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User not exists by Username");
}
Set<GrantedAuthority> authorities = user.getRoles().stream()
.map((role) -> new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName()))
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(username,user.getPassword(),authorities);
}
}8. Create a DTO class
LoginDto.java
package com.springjava.dto;
public class LoginDto {
private String username;
private String password;
public LoginDto() { }
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}SignUpDto.java
package com.springjava.dto;
public class SignUpDto {
private String name;
private String username;
private String email;
private String password;
public SignUpDto() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}9. Create a Controller class
HomeController.java
package com.springjava.controller;
import java.util.Collections;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.springjava.dto.LoginDto;
import com.springjava.dto.SignUpDto;
import com.springjava.entity.Role;
import com.springjava.entity.User;
import com.springjava.repository.RoleRepository;
import com.springjava.repository.UserRepository;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class HomeController {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Autowired
private RoleRepository roleRepository;
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@PostMapping("/login")
public ResponseEntity<String> authenticateUser(@RequestBody LoginDto loginDto) {
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager
.authenticate(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(loginDto.getUsername(), loginDto.getPassword()));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
return new ResponseEntity<>("User login successfully!...", HttpStatus.OK);
}
@PostMapping("/signup")
public ResponseEntity<?> registerUser(@RequestBody SignUpDto signUpDto){
// checking for username exists in a database
if(userRepository.existsByUserName(signUpDto.getUsername())){
return new ResponseEntity<>("Username is already exist!", HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
// checking for email exists in a database
if(userRepository.existsByEmail(signUpDto.getEmail())){
return new ResponseEntity<>("Email is already exist!", HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
// creating user object
User user = new User();
user.setName(signUpDto.getName());
user.setUserName(signUpDto.getUsername());
user.setEmail(signUpDto.getEmail());
user.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(signUpDto.getPassword()));
Role roles = roleRepository.findByName("ROLE_ADMIN").get();
user.setRoles(Collections.singleton(roles));
userRepository.save(user);
return new ResponseEntity<>("User is registered successfully!", HttpStatus.OK);
}
}10. Create a Spring Security Config class
SecurityConfig.java
package com.springjava.security;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.configuration.AuthenticationConfiguration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public static PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager(AuthenticationConfiguration configuration) throws Exception {
return configuration.getAuthenticationManager();
}
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/api/**", "/h2-console/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
http.headers().frameOptions().disable();
return http.build();
}
}11. Insert data in the database using SpringBootApplication class
package com.springjava;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import com.springjava.entity.Role;
import com.springjava.repository.RoleRepository;
@SpringBootApplication
public class LoginRegistrationRestApiSpringSecurityApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(LoginRegistrationRestApiSpringSecurityApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner demo(RoleRepository roleRepo) {
return (args) -> {
Role role=new Role();
role.setName("ROLE_ADMIN");
roleRepo.save(role);
};
}
}12. Run the Application
To run this application right-click on the SpringBootApplication class, click Run As, then select the Java Application option.
Testing the API in Postman
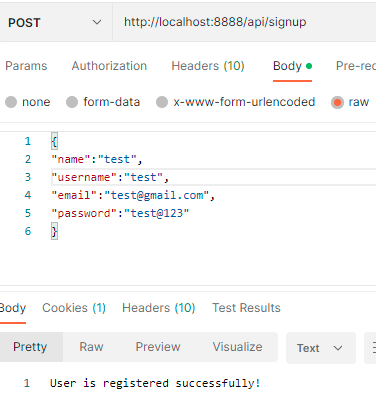
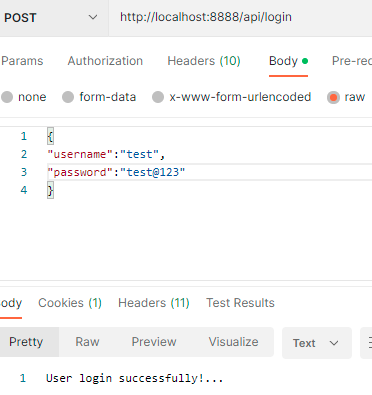
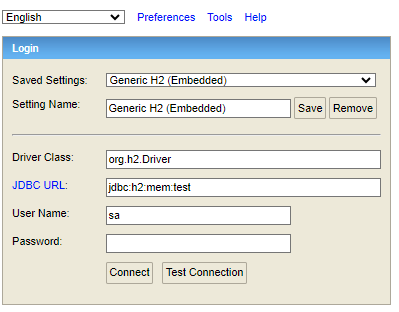
To Check the H2 Database browse this URL http://localhost:8888/h2-console/
13. Conclusion
In this example, we learnt how to implement spring security login and registration rest API in the spring boot example.

Howdy! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept chatting about this. I will forward this write-up to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
I need to to thank you for this excellent read!! I definitely loved every little bit of it. I have you book-marked to look at new things you post…
I used to be suggested this website through my cousin. I’m no longer sure whether this submit is written through him as nobody else know such precise approximately my trouble. You’re amazing! Thank you!
Wow, this post is fastidious, my sister is analyzing these things, thus I am going to convey her.
Appreciate the recommendation. Will try it out.
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to assert that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently rapidly.
Good answers in return of this issue with solid arguments and describing everything about that.
Hurrah! In the end I got a weblog from where I be able to really take helpful facts concerning my study and knowledge.
Hi there, everything is going perfectly here and ofcourse every one is sharing facts, that’s actually excellent, keep up writing.
It’s awesome for me to have a website, which is useful in support of my experience. thanks admin
Hello there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I’m not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my difficulty. You are incredible! Thanks!
I am truly grateful to the holder of this web page who has shared this fantastic post at at this place.
Excellent post. I was checking constantly this blog and I am impressed! Extremely helpful info specially the last part 🙂 I care for such info a lot. I was looking for this certain information for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.
I like the valuable info you provide in your articles. I will bookmark your blog and check again here frequently. I am quite certain I will learn lots of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
Thanks for a marvelous posting! I seriously enjoyed reading it, you may be a great author.I will ensure that I bookmark your blog and will often come back down the road. I want to encourage one to continue your great posts, have a nice afternoon!
What a stuff of un-ambiguity and preserveness of valuable know-how concerning unexpected emotions.
What’s up Dear, are you genuinely visiting this site daily, if so afterward you will without doubt obtain nice experience.
Hello there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I’m gonna watch out for brussels. I’ll appreciate if you continue this in future. Many people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
This excellent website definitely has all of the information and facts I needed about this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Hi there all, here every person is sharing these knowledge, so it’s good to read this weblog, and I used to go to see this web site all the time.
Appreciate this post. Will try it out.
I am extremely inspired along with your writing talents and also with the format in your blog. Is that this a paid topic or did you modify it your self? Anyway keep up the nice high quality writing, it’s rare to see a great weblog like this one today..
I am regular visitor, how are you everybody? This piece of writing posted at this web site is truly good.
I like what you guys tend to be up too. Such clever work and exposure! Keep up the amazing works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to our blogroll.
Hey there, You’ve done an excellent job. I will definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m confident they will be benefited from this site.
I am not sure where you are getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more. Thanks for magnificent information I was looking for this info for my mission.
Article writing is also a excitement, if you be acquainted with after that you can write otherwise it is difficult to write.
Someone necessarily lend a hand to make severely posts I would state. This is the first time I frequented your web page and so far? I surprised with the analysis you made to make this actual publish incredible. Wonderful activity!
If some one wants expert view regarding blogging afterward i recommend him/her to pay a visit this website, Keep up the good work.
An outstanding share! I have just forwarded this onto a co-worker who had been conducting a little research on this. And he actually ordered me lunch due to the fact that I found it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending the time to discuss this topic here on your site.
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d definitely donate to this fantastic blog! I suppose for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to brand new updates and will talk about this site with my Facebook group. Talk soon!
Everything is very open with a precise explanation of the challenges. It was definitely informative. Your website is very helpful. Thanks for sharing!
I am in fact grateful to the owner of this web site who has shared this wonderful article at here.
Hello, its pleasant paragraph concerning media print, we all be aware of media is a impressive source of data.
It’s very effortless to find out any topic on net as compared to books, as I found this post at this web site.
Can I simply say what a comfort to find someone who truly knows what they are talking about over the internet. You definitely realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. A lot more people ought to look at this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised you’re not more popular given that you surely have the gift.
I really like reading through a post that will make people think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I have really enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again very soon!
It’s amazing to pay a visit this web site and reading the views of all friends on the topic of this paragraph, while I am also keen of getting know-how.
Hi, everything is going fine here and ofcourse every one is sharing data, that’s really excellent, keep up writing.
Wow, incredible blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is fantastic, let alone the content!
Hello, I log on to your blog like every week. Your story-telling style is witty, keep up the good work!
I love it when folks come together and share views. Great blog, continue the good work!
This piece of writing is genuinely a pleasant one it helps new net people, who are wishing in favor of blogging.
I’m now not sure the place you are getting your information, however good topic. I must spend a while finding out more or figuring out more. Thank you for fantastic info I was in search of this info for my mission.
These are truly fantastic ideas in regarding blogging. You have touched some good factors here. Any way keep up wrinting.
I’m gone to inform my little brother, that he should also go to see this blog on regular basis to obtain updated from most recent news.
It’s not my first time to visit this web page, i am visiting this web page dailly and obtain fastidious facts from here every day.
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my blog thus i came to “return the favor”.I am trying to find things to enhance my site!I suppose its ok to use some of your ideas!!
Nice blog here! Also your website loads up very fast! What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my website loaded up as quickly as yours lol
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You obviously know what youre talking about, why waste your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
It’s hard to come by educated people about this subject, however, you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Yes! Finally something about вавада.
Good article! We are linking to this particularly great post on our website. Keep up the good writing.
excellent publish, very informative. I wonder why the other experts of this sector don’t understand this. You must continue your writing. I am sure, you have a huge readers’ base already!
hi!,I love your writing so a lot! percentage we communicate more approximately your article on AOL? I need a specialist on this space to unravel my problem. May be that is you! Taking a look forward to look you.
Hey! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone 4! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Carry on the great work!
This page definitely has all the information I needed concerning this subject and didn’t know who to ask.
Asking questions are in fact fastidious thing if you are not understanding something totally, but this piece of writing presents pleasant understanding yet.
Every weekend i used to pay a visit this site, as i wish for enjoyment, since this this web page conations truly pleasant funny information too.
I’m curious to find out what blog platform you happen to be working with? I’m having some minor security problems with my latest blog and I’d like to find something more safe. Do you have any recommendations?
Thanks in support of sharing such a pleasant thought, paragraph is good, thats why i have read it completely
When someone writes an article he/she maintains the idea of a user in his/her brain that how a user can know it. So that’s why this article is great. Thanks!
Thank you for the good writeup. It actually was a amusement account it. Glance complicated to far added agreeable from you! By the way, how can we keep in touch?
Hi everyone, it’s my first visit at this website, and article is truly fruitful for me, keep up posting these articles or reviews.
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an really long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say excellent blog!
Valuable info. Lucky me I discovered your site accidentally, and I am stunned why this coincidence did not happened in advance! I bookmarked it.
Everything is very open with a really clear explanation of the challenges. It was really informative. Your site is very useful. Thanks for sharing!
Hi there it’s me, I am also visiting this site daily, this website is really pleasant and the users are truly sharing pleasant thoughts.
I was suggested this blog by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my trouble. You’re incredible! Thanks!
My relatives every time say that I am wasting my time here at web, however I know I am getting familiarity everyday by reading such pleasant articles.
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own weblog and was curious what all is required to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very web smart so I’m not 100% certain. Any recommendations or advice would be greatly appreciated. Cheers
Hey there are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you require any html coding knowledge to make your own blog? Any help would be really appreciated!
Hi there! Quick question that’s entirely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My website looks weird when viewing from my iphone. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to resolve this issue. If you have any suggestions, please share. Many thanks!
fantastic put up, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector do not notice this. You must proceed your writing. I’m confident, you have a huge readers’ base already!
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon!
Greetings, I believe your website could be having internet browser compatibility problems. When I look at your web site in Safari, it looks fine however, if opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to give you a quick heads up! Apart from that, fantastic website!
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It absolutely useful and it has aided me out loads. I am hoping to contribute & assist other users like its helped me. Great job.
My programmer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the costs. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on various websites for about a year and am nervous about switching to another platform. I have heard fantastic things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress posts into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
Just desire to say your article is as amazing. The clearness in your post is just excellent and i can assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the enjoyable work.
What’s up, just wanted to tell you, I enjoyed this article. It was practical. Keep on posting!
My developer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using WordPress on a variety of websites for about a year and am nervous about switching to another platform. I have heard good things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can transfer all my wordpress posts into it? Any help would be really appreciated!
Hi to every body, it’s my first pay a visit of this blog; this blog consists of amazing and actually fine material designed for readers.
I really like what you guys are up too. Such clever work and coverage! Keep up the wonderful works guys I’ve added you guys to our blogroll.
Hello there! This article couldn’t be written any better! Looking at this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I am going to forward this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Howdy! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all folks you actually realize what you’re talking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly also consult with my website =). We will have a hyperlink exchange contract among us
Very nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wanted to mention that I’ve truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts. After all I’ll be subscribing for your rss feed and I hope you write again soon!
I could not refrain from commenting. Perfectly written!
В Aurora Casino каждый момент полон волнения, а каждый спин может привести к значительному выигрышу. Наши пользователи могут наслаждаться множеством разнообразных игр, включая слоты, рулетку и покер с живыми дилерами. Не забывайте о бонусах и промо-акциях, которые принесут вам дополнительные возможности для победы.
Почему стоит выбрать именно Аврора играйте бесплатно? В Aurora Casino ваши средства и личная информация находятся под надежной защитой, а игры проходят в честных условиях. Мы стараемся сделать каждый игровой процесс интересным и доступным для наших клиентов.
Когда стоит начать свой путь в Aurora Casino? Зарегистрируйтесь и получите доступ ко всем возможностям, которые мы предлагаем нашим игрокам. Вот что вас ожидает:
Сразу после регистрации вы получите бонусы и сможете участвовать в акциях.
Постоянные турниры с большими призами.
Новые игры и регулярные обновления.
Aurora Casino — это место, где каждый найдет для себя что-то увлекательное и прибыльное.
I’m amazed, I must say. Seldom do I come across a blog that’s both educative and engaging, and without a doubt, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The issue is an issue that too few folks are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy that I found this during my hunt for something relating to this.
It’s the best time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I wish to suggest you few interesting things or suggestions. Maybe you can write next articles referring to this article. I desire to read even more things about it!
Hi! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog article or vice-versa? My blog goes over a lot of the same topics as yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other. If you happen to be interested feel free to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Excellent blog by the way!
Excellent post. Keep writing such kind of information on your blog. Im really impressed by your site.
Hi there, You have performed a great job. I will certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m confident they’ll be benefited from this web site.
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyways, just wanted to say excellent blog!
I was recommended this web site by means of my cousin. I’m no longer certain whether or not this submit is written via him as nobody else understand such detailed approximately my difficulty. You’re incredible! Thank you!
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all of us you actually realize what you are talking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly also visit my web site =). We will have a link change agreement between us
I think this is among the most important info for me. And i’m glad reading your article. But wanna remark on some general things, The site style is ideal, the articles is really excellent : D. Good job, cheers