In this example, we will learn how to implement login REST API with database authentication using spring security in the spring boot example.
Table of Content
1. Keep Eclipse IDE ready(STS integrated)
2. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
3. Maven Dependency
4. Define Database configuration in the application.properties file
5. Create entity class
6. Create a repository
7. Create a service
8. Create a DTO class
9. Create a Controller class
10. Create a Spring Security Config class
11. Insert data into the database
12. Run the Application
13. Conclusion
1. Keep Eclipse IDE ready(STS integrated)
Refer to this article How to Create Spring Project in IDEto create Spring Boot Project in Eclipse IDE.
2. Create a Spring Boot Starter Project
Add the following dependencies:
• Spring Web
• Spring Security
• MySQL Driver
• Spring Data JPA
Project Structure of Login Rest Api with Spring Security
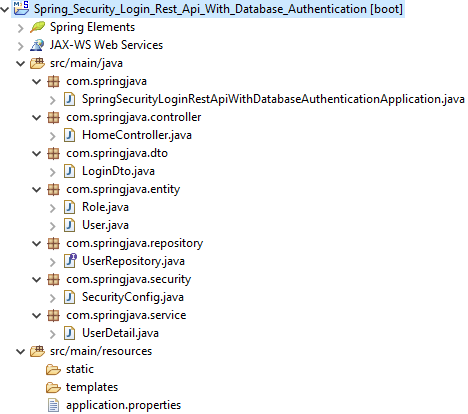
3. Maven Dependency
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.11</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.springjava</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring_Security_Login_Rest_Api_With_Database_Authentication</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Spring_Security_Login_Rest_Api_With_Database_Authentication</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>16</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<!-- <scope>runtime</scope> -->
<version>5.1.32</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4. Define Database configuration in the application.properties file
#Mysql Database
spring.datasource.driver-class-name= com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/poc_db?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=mysql
hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=true
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
server.port=88885. Create entity class
Role.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Role {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Role() {
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}User.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany;
import org.hibernate.annotations.LazyCollection;
import org.hibernate.annotations.LazyCollectionOption;
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String username;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String email;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String password;
@ManyToMany
@LazyCollection(LazyCollectionOption.FALSE)
private Set<Role> roles;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Set<Role> getRoles() {
return roles;
}
public void setRoles(Set<Role> roles) {
this.roles = roles;
}
}6. Create a repository
UserRepository.java
package com.springjava.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springjava.entity.User;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> {
User findByUsernameOrEmail(String username, String email);
}7. Create a service
UserDetail.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springjava.entity.User;
import com.springjava.repository.UserRepository;
@Service
public class UserDetail implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepo;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username)throws UsernameNotFoundException{
User user = userRepo.findByUsernameOrEmail(username, username);
if(user==null){
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User not exists by Username");
}
Set<GrantedAuthority> authorities = user.getRoles().stream()
.map((role) -> new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName()))
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(username,user.getPassword(),authorities);
}
}8. Create a DTO class
LoginDto.java
package com.springjava.dto;
public class LoginDto {
private String username;
private String password;
public LoginDto() {
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}9. Create a Controller class
HomeController.java
package com.springjava.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.springjava.dto.LoginDto;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class HomeController {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@PostMapping("/login")
public ResponseEntity<String> authenticateUser(@RequestBody LoginDto loginDto){
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
loginDto.getUsername(), loginDto.getPassword()));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
return new ResponseEntity<>("User login successfully!.", HttpStatus.OK);
}
}10. Create a Spring Security Config class
SecurityConfig.java
package com.springjava.security;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.configuration.AuthenticationConfiguration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public static PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager(AuthenticationConfiguration configuration) throws Exception {
return configuration.getAuthenticationManager();
}
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/api/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
return http.build();
}
}11. Insert data into the database
INSERT INTO `user` VALUES
(1,'admin@gmail.com','admin','$2a$10$gqHrslMttQWSsDSVRTK1OehkkBiXsJ/a4z2OURU./dizwOQu5Lovu','admin'),
(2,'test@gmail.com','test'$2a$12$TYSPPDsgR1T9vpgMSavOteZoqzjGVLt7rzsqKLrGL4oQdE3rWDNru','test');
INSERT INTO `role` VALUES (1,'ROLE_ADMIN'),(2,'ROLE_USER');
INSERT INTO `user_role` VALUES (1,1),(2,2);12. Run the Application
To run this application right-click on the application, click Run As, then select the Java Application option.
Testing the API in Postman
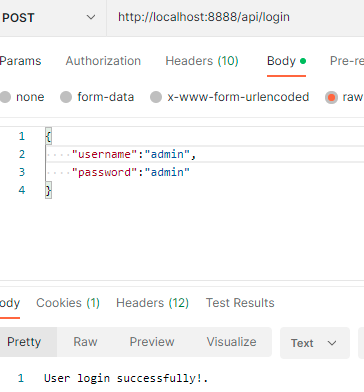
13. Conclusion
In this example, we learnt how to implement spring security login rest API with database authentication in the spring boot example.
