Last updated on April 24th, 2024
In the JPA Repository, if we need to fetch records based on the find by list of ids from the database table, we can use the findAllById query method. This findAllById is a ready-made method provided by Spring Data JPA to select the records by passing a list of ids. In this topic, we will learn how to implement JPA Repository find by list of ids using Spring Boot, Maven, Spring Web, Lombok, Spring Data JPA and H2 database.
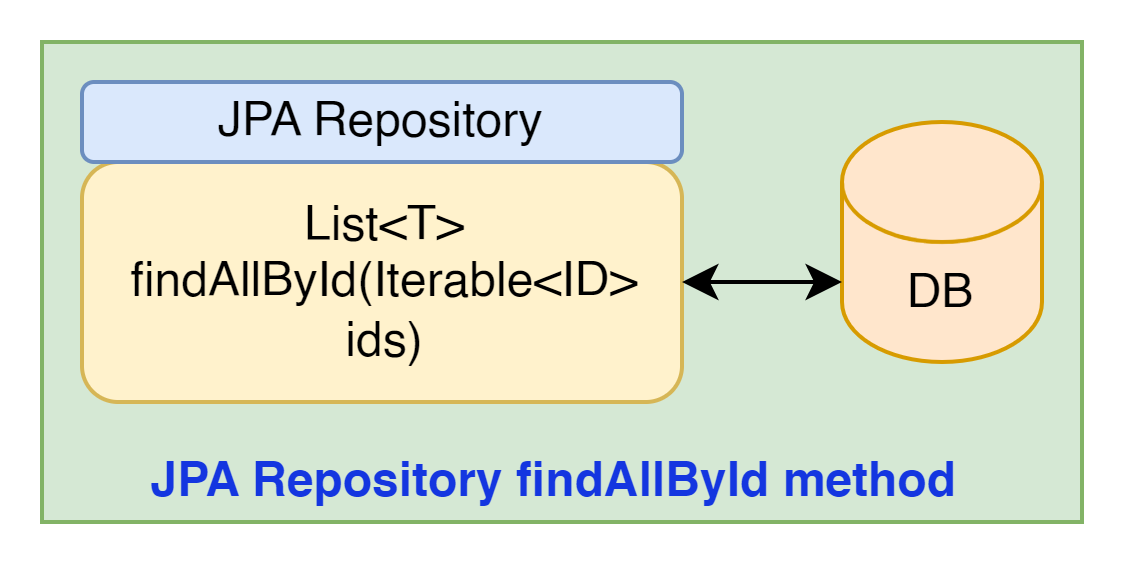
JPA Repository findAllById method
List<T> findAllById(Iterable<ID> ids)- This method returns all instances of the type T with the provided IDs.
- If in case some or all ids are not found, no entities are returned for these provided IDs.
- The order of elements in the result is not guaranteed by this method.
- The CrudRepository interface of Spring Data JPA specifies this method.
- The parameter ids must not be null nor contain any null values.
- The method returns guaranteed to be not null. A size can be equal to or less than the number of given ids.
- This method throws IllegalArgumentException if the given ids or one of its items is null.
Let’s create a restful web service Spring Boot application to fetch a list of employees by the list of ids using the JPA Repository query method findAllById(-) step-by-step.
These are the following steps:
- Creating a Spring Boot Starter Project
- Keep the IDE ready
- Maven Dependency
- Defining the configuration
- Creating a JPA Entity
- Creating a JPA Repository
- Creating a Service Interface
- Creating a Service class
- Creating a Rest Controller class
- Run the Spring Application and Check
1. Creating a Spring Boot Starter Project
We are creating a Spring Boot Application from the web tool Spring Initializr or you can create it from the IDE(STS, VS Code etc.) you are using.
Add the following dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Data JPA
- Lombok
- H2 Database
2. Keep the IDE ready
We are importing this created application into our Eclipse IDE or you can import it into another IDE you are using. You can refer to this article to create and set up the Spring Boot Project in Eclipse IDE.
Project Structure of Find By List of Ids
3. Maven Dependency
Here is the complete pom.xml file for the Spring Boot Application.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
<relativePath />
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.springjava</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4. Defining the configuration
We are configuring the H2 database configuration in the application.properties file.
application.properties
# H2 Database Configuration
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:test
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.h2.console.enabled=true5. Creating a JPA Entity
We are creating a JPA entity class Employee with these properties(id, firstName,lastName, email and department).
Employee.java
package com.springjava.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@Entity
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private String department;
}- This @Data annotation is used for a constructor, setter method, getter method, etc.
- This @Entity annotation is used to create a table through Java code in the database.
6. Creating a JPA Repository
We are a JPA Repository to interacts with the JPA Entity class and use its query methods(save() and findAllById()).
EmplRepository.java
package com.springjava.repository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import com.springjava.entity.Employee;
public interface EmplRepository extends JpaRepository < Employee, Long > {
}7. Creating a Service Interface
We are creating a Service interface with some method declaration(save(Employee employee) and getByListOfIds(List<Long> ids)). So the implementation class of this interface overrides these declared methods in there.
EmployeeService.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import com.springjava.entity.Employee;
public interface EmployeeService {
void save(Employee employee);
List < Employee > getByListOfIds(List < Long > ids);
}8. Creating a Service class
We are creating a Service class EmployeeServiceImpl and this class is implementing the EmployeeService interface. This class is annotated with @Service annotation to act service.
EmployeeServiceImpl.java
package com.springjava.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springjava.entity.Employee;
import com.springjava.repository.EmplRepository;
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmplRepository empRepo;
@Override
public void save(Employee employee) {
empRepo.save(employee);
}
@Override
public List < Employee > getByListOfIds(List < Long > ids) {
return empRepo.findAllById(ids);
}
}- We used @Autowired annotation to inject the EmplRepository in this service class.
- We used save() and findAllById() query methods of that JPA Repository.
9. Creating a Rest Controller class
We are creating a RestController class EmployeeController in which all methods are created for API endpoints for handling requests from the clients.
EmployeeController.Java
package com.springjava.controller;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.springjava.entity.Employee;
import com.springjava.service.EmployeeService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/employee")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
EmployeeService empService;
@PostMapping("/save")
public ResponseEntity < ? > save(@RequestBody Employee employee) {
Map < String, Object > respEmp = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
empService.save(employee);
respEmp.put("status", 1);
respEmp.put("message", "Record is Saved Successfully!");
return new ResponseEntity < > (respEmp, HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@GetMapping("/find-by-list-of-ids")
public ResponseEntity < ? > getByListOfIds() {
Map < String, Object > respEmp = new LinkedHashMap < String, Object > ();
List < Long > ids = Arrays.asList(1 L, 2 L);
List < Employee > emList = empService.getByListOfIds(ids);
if (!emList.isEmpty()) {
respEmp.put("status", 1);
respEmp.put("data", emList);
return new ResponseEntity < > (respEmp, HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
respEmp.clear();
respEmp.put("status", 0);
respEmp.put("message", "Data is not found");
return new ResponseEntity < > (respEmp, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
}- This class is annotated with @RestController annotation to make this class act as Rest Controller for giving responses in JSON form.
- We used @RequestMapping annotation to define the base URL for the application.
- We used @PostMapping and @GetMapping annotations to handle HTTP requests from the client.
- We used ResponseEntity to represent the entire HTTP response.
- We used @Autowired annotation to inject EmployeeService into the class.
- We used @RequestBody annotation to take JSON object in the save() method as the parameter of the Employee class.
- We have created two restful web services handling methods(save() and getByListOfIds()).
- save(): This saves Employee records into the database.
- getByListOfIds(): This fetches a list of Employee records by passing the list of ids as a parameter.
10. Run the Spring Boot Application and Check
Right-click this Spring Boot application on the DemoApplication.java, then click RunAs and select Java Application.
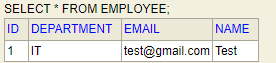
Check H2 Database
Check the H2 database console and browse this URL “http://localhost:8080/h2-console”.
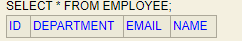
See the below table here:
Testing API on the Postman
Saving the employee data
POST: http://localhost:8080/api/employee/save
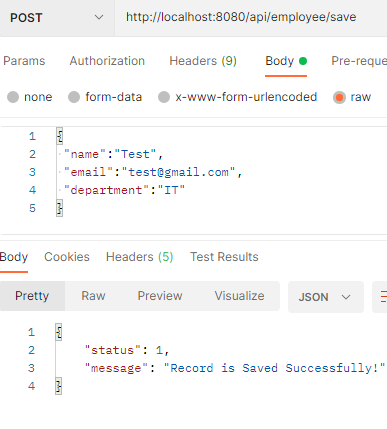
Check the table:
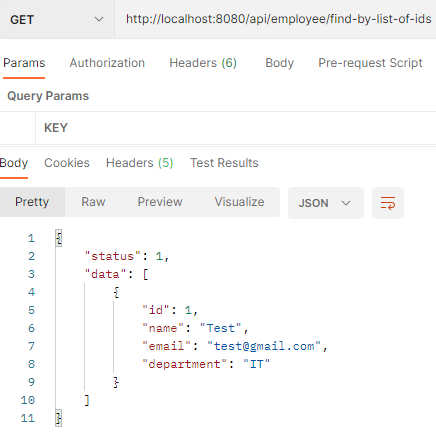
Retrieving the employees by the list of Ids
GET: http://localhost:8080/api/employee/find-by-list-of-ids
After this API hit Spring Data JPA (internally uses Hibernate as a JPA provider) generated SQL statement in the console below here:
Hibernate:
select employee0_.id as id1_0_,
employee0_.department as departme2_0_,
employee0_.email as email3_0_,
employee0_.name as name4_0_
from
employee employee0_
where
employee0_.id in (? , ?)Conclusion
In this topic, we learned how to use the JPA Repository findAllById method in the Spring Boot Restful web services application.
